|
Nitrogen atom structure
Wave theory-United nature theory
Tejman Chaim Henry Dr.
Name:
Nitrogen
Symbol:
N
Atomic Number:
7
Atomic Mass:
14.00674 amu
Melting Point:
-209.9 °C (63.250008 K, -345.81998 °F)
Boiling Point:
-195.8 °C (77.35 K, -320.44 °F)
Number of
Protons/Electrons: 7
Number of Neutrons:
7
Classification:
Non-metal
Crystal Structure:
Hexagonal
Density @ 293 K:
1.2506 g/cm3
Color:
colorless
Atom structure needs a lot of imagination
and common sense for understand atom–quantum{gravitational wave} behaviour. Every
atom is specific quantum formation with specific all dimensions and space
time geometry.{A. Einstein}.
|
Isotope
|
Half
Life
|
|
N-13
|
9.97 minutes
|
|
N-14
|
Stable
|
|
N-15
|
Stable
|
|
N-16
|
7.13 seconds
|
Date of Discovery:
1772
Discoverer:
Daniel Rutherford
Name Origin:
Greek
Uses:
forms most of atmosphere
Obtained From:
from liquid air
http://www.chemicalelements.com/elements/n.html
Structure of Nitrogen
·
Atomic
Radius: 0.75Å
·
Atomic
Volume: 17.3cm3/mol
·
Covalent
Radius: 0.75Å
·
Cross
Section (Thermal Neutron Capture)  a/barns: 1.91 a/barns: 1.91
·
Crystal
Structure: Hexagonal
·
Electron Configuration:
1s2 2s2p3
·
Electrons per Energy
Level: 2,5
Shell
Model
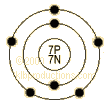
·
Ionic
Radius: 0.13Å
·
Filling
Orbital: 2p3
·
Number of Electrons
(with no charge): 7
·
Number of Neutrons
(most common/stable nuclide): 7
·
Number of Protons: 7
·
Oxidation
States: ±3,5,4,2
·
Valence
Electrons: 2s2p3
Electron
Dot Model

Chemical Properties of Nitrogen
·
Electrochemical
Equivalent: 0.10452g/amp-hr
·
Electron
Work Function:
·
Electronegativity: 3.04 (Pauling); 3.07 (Allrod Rochow)
·
Heat
of Fusion: 0.3604kJ/mol
·
Incompatibilities:
·
Ionization Potential
o
First: 14.534
o
Second: 29.601
o
Third: 47.448
·
Valence
Electron Potential (-eV): 550
Physical Properties of Nitrogen
·
Atomic
Mass Average: 14.00674
·
Boiling
Point: 77.5K
-195.65°C
-320.17°F
·
Coefficient
of lineal thermal expansion/K-1: N/A
·
Conductivity
Electrical:
Thermal: 0.0002598 W/cmK
·
Density: 1.2506g/L @ 273K & 1atm
·
Description:
Colorless, odorless,
tasteless gas
http://environmentalchemistry.com/yogi/periodic/N.html
l
|

|
The structure of like
H. Atom
I describe on
Basis M-51 galaxy.
Small and large formations must have
The same behavior.
{A. Einstein}
This galaxy
clearly
show two different swirls connected by two energetic
path and is completely independent wave
{Quantum} formation.
=.
|
The structure of like H. Atom
Helium atom
Lithium atom strcture
Beryllium atom structure
See H, He, Li atoms {Tejman}.
Beryllium atom structure
Boron atom structure
Boron atom structure
Carbon atom structure
Carbon atom structure
Nitrogen atom
|
Isotope
|
Half
Life
|
|
N-13
|
9.97 minutes
|
|
N-14
|
Stable
|
|
N-15
|
Stable
|
|
N-16
|
7.13 seconds
|
|

|

|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Instead of
neutron wz particle
|
stabile
|
2-neutrons
|
2-netrons +
wz-particle
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Summary:
Nitrogen is the most important atom for life
creation.
© Copyright:
Dr. Tejman Chaim, Henry August 2007
http://www.grandunifiedtheory.org.il/
The theory of everything
|